Unraveling Resistors in AC Circuits: Operational Principles and Illustrative Examples
Resistors play a fundamental role in AC (alternating current) circuits. When it comes to their working in AC circuits, the basic principle remains similar to that in DC circuits in some aspects. Resistors oppose the flow of electric current. In an AC circuit, as the voltage continuously alternates its polarity and magnitude sinusoidally with a specific frequency, the resistor restricts the flow of electrons in accordance with Ohm's law, which states that the current (I) through a resistor is equal to the voltage (V) across it divided by its resistance (R), i.e., I = V/R.
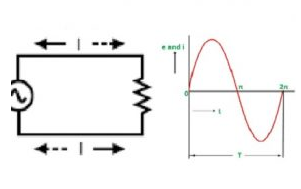
The key difference in AC is that both the voltage and current are constantly changing. However, the resistance value of a resistor, which is a property depending on its physical construction and material, remains constant regardless of the alternating nature of the current. So, for each instantaneous value of the AC voltage, the resistor instantaneously determines the corresponding current value.
For example, consider a simple household lighting circuit where an incandescent bulb is connected in series with a resistor. The AC voltage from the mains supply (usually 110V or 220V with a frequency of 50Hz or 60Hz depending on the region) drives current through the circuit. The resistor here can be used to limit the current flowing through the bulb to prevent it from burning out due to excessive current. If the bulb has a rated power and voltage, by calculating the appropriate resistance value, we can ensure it operates within its designed parameters.
Another example is in an audio amplifier circuit. AC signals representing sound waveforms pass through various resistors. These resistors are used for tasks like voltage division to set proper biasing levels for transistors within the amplifier. They help shape the amplitude and frequency response of the audio signal, ensuring that the amplified sound is clear and distortion-free. Resistors in such circuits interact with other components like capacitors and inductors to precisely control the flow and characteristics of the AC audio signals, allowing for high-fidelity sound reproduction.
Email us
 RXF21A/B/C (FRT) wire - wound fusing resistors
RXF21A/B/C (FRT) wire - wound fusing resistors RFX21-T low-power full-short-circuit resistors
RFX21-T low-power full-short-circuit resistors RFX21-D semi-short-circuit surge-resistant wirewound resistors
RFX21-D semi-short-circuit surge-resistant wirewound resistors RF10 painted thin-film fuse resistors
RF10 painted thin-film fuse resistors RF11 porcelain-cased thin-film fuse resistors
RF11 porcelain-cased thin-film fuse resistors RWF molded wirewound fuse resistors
RWF molded wirewound fuse resistors RXG21 (A/B/C/D) lightning surge-resistant wirewound resistors
RXG21 (A/B/C/D) lightning surge-resistant wirewound resistors RXF21-TE power-type full-short-circuit temperature fuse resistors
RXF21-TE power-type full-short-circuit temperature fuse resistors RX22 Vitreous enameled wire - wound resistors
RX22 Vitreous enameled wire - wound resistors RX23 ceramic encased wire - wound resistors
RX23 ceramic encased wire - wound resistors RX92 anti - interference wire - wound resistors
RX92 anti - interference wire - wound resistors RX21 coated wire - wound resistors
RX21 coated wire - wound resistors RXLG high power aluminum encased wire - wound resistors
RXLG high power aluminum encased wire - wound resistors RX27 power ceramic encased wire - wound resistors
RX27 power ceramic encased wire - wound resistors RXL power aluminum encased wire - wound resistors
RXL power aluminum encased wire - wound resistors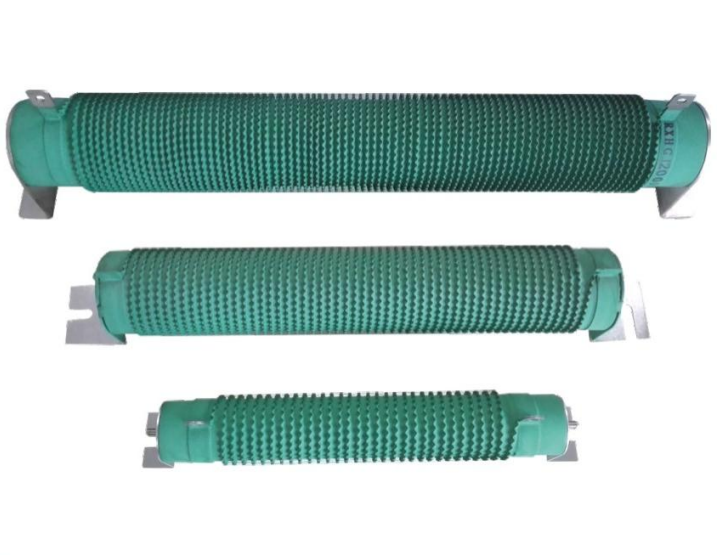 RXHGI high power wane ripple coated wire - wound resistors
RXHGI high power wane ripple coated wire - wound resistors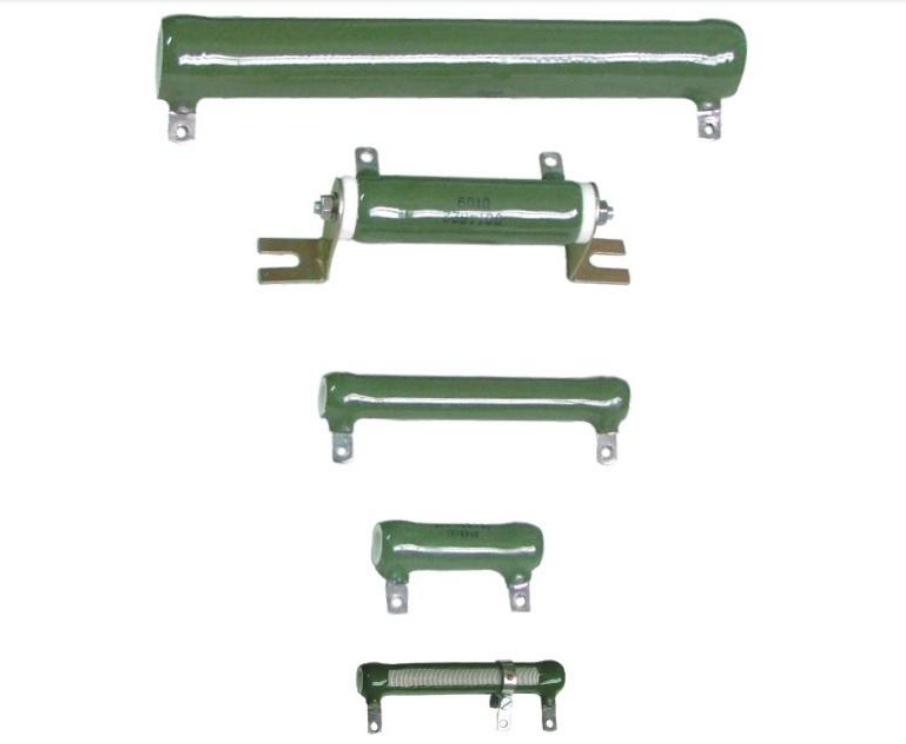 RX20 high power vitreous enameled wire - wound resistors
RX20 high power vitreous enameled wire - wound resistors RX24 aluminum encased power wire - wound resistors
RX24 aluminum encased power wire - wound resistors RXLB power aluminum encased wire - wound resistors
RXLB power aluminum encased wire - wound resistors RXBRXB1 Flat coated wire - wound resistors
RXBRXB1 Flat coated wire - wound resistors REWR huge power circular edge wound resistors
REWR huge power circular edge wound resistors RXGI high power coated wire - wound resistors
RXGI high power coated wire - wound resistors RXGM high power coated wire - wound resistors
RXGM high power coated wire - wound resistors REW600 water cooled power resistors wirewound, aluminum
REW600 water cooled power resistors wirewound, aluminum
- High Precision Metal Film Resistors: Ultimate Accuracy for Critical Circuits
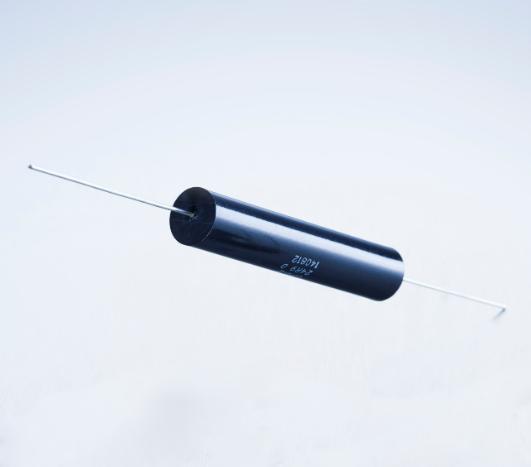

High precision metal film resistors are applicable to fields such as analog signal acquisition and precision instruments and meters.● Products with military standard certification.● High stability...
- High Precision Metal Film Resistors: Optimal Performance for Analog and RF Circuits

In the complex and demanding realm of electronic circuits, high precision metal film resistors have emerged as a linchpin, particularly when it comes to analog and RF (Radio Frequency) circuits, where...
Resistor Supplies - Jepsun Tech Corporation
JEPSUN INDUSTRIAL is committed to always being one of our customers' favorite suppliers.
+86755-29796190 +8615920026751 [email protected]
Huangjiazhongxin building Donghuan Road Longhua District SHENZHEN City, GUANGDONG Prov. CHINA 518000